The exchange rate system is a key aspect of the foreign exchange market. The term Exchange rate actually refers to the rate at which the currency of a country gets converted into another country’s currency. Mainly there are two most commonly used types of exchange rate i.e. fixed exchange rate and flexible exchange rate. In this article, we will explore the complete difference between fixed and flexible exchange rate, their advantages and disadvantages, and their basic concepts. So let’s first have a look at a table comparing both fixed vs flexible exchange rate in a brief manner.
Fixed Vs Flexible Exchange Rate (Comparison Chart)
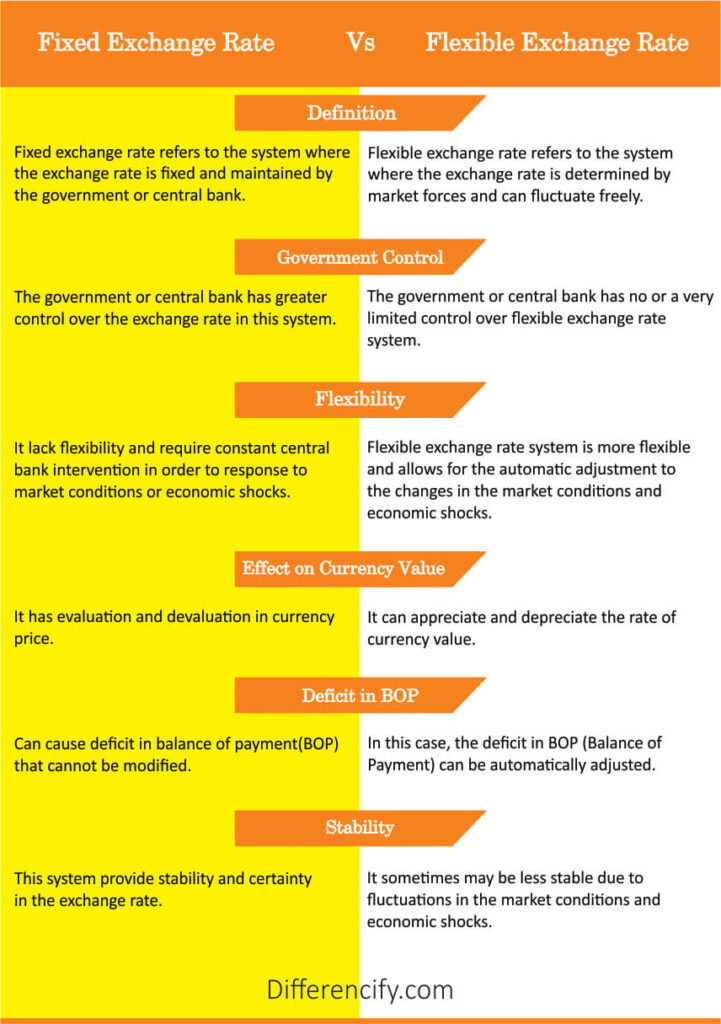
| Fixed Exchange Rate | Flexible Exchange Rate |
|---|---|
| A fixed exchange rate refers to a system where the exchange rate is fixed and maintained by the government or central bank. | A flexible exchange rate refers to a system where the exchange rate is determined by market forces and can fluctuate freely. |
| The government or central bank has greater control over the exchange rate in this system. | The government or central bank has no or very limited control over the flexible exchange rate system. |
| Fixed exchange rate systems lack flexibility and require constant central bank intervention in order to respond to market conditions and economic shocks. | A flexible exchange rate is more flexible and allows for automatic adjustment to changes in market conditions or economic shocks. |
| It has a valuation or devaluation in currency price. | It can appreciate or depreciate the rate of currency value. |
| Fixed exchange rates may cause a deficit in the Balance of Payment (BOP) that cannot be modified. | In the case of a flexible exchange rate, the deficit in the Balance of Payment (BOP) can be automatically adjusted. |
| It provides stability and certainty in the exchange rate. | It sometimes may be less stable due to fluctuations in market conditions and economic shocks. |
- Difference Between Fixed and Flexible Budget
- Financial Vs Management Accounting
- Market Vs Command Economy
What is a Fixed Exchange Rate?
A fixed exchange rate system is a monetary system in which the value of a currency is fixed to another currency, a basket of currencies, or gold. In other words, fixed exchange rate refers to the nominal exchange system wherein the government and other monetary authorities like the central bank try to keep the rate of state currency fixed against the rate/value of other currencies. This means that the fixed exchange rate is only set by the government and other competent authorities and it can never be determined by market forces.
Under this system, the IMF(International Monetary Fund) management allows the flexibility of exchange rate(if any) to a country, but up to a certain level. Moreover, a fixed exchange rate regime helps to provide a credible point for low-inflationary monetary policy by reducing the transaction cost caused due to exchange rate uncertainty. Another term that can be used for a fixed exchange rate is Pegged Exchange Rate.
Pros of Fixed Exchange Rate
- Certainty and Stability – One of the primary advantages of a fixed exchange rate system is the certainty and stability it provides. Businesses and individuals can plan their transactions with confidence, knowing that the exchange rate will remain constant.
- Price Stability – Another advantage of a fixed exchange rate system is that it can help to promote price stability. Because the exchange rate is fixed, it is easier for the central bank to control inflation.
- Encourages Foreign Investment – Fixed exchange rates can also encourage foreign investment. When investors have confidence in a country’s exchange rate stability, they are more likely to invest in that country.
Cons of Fixed Exchange Rate
The two common disadvantages of fixed exchange rates are as follows.
- Lack of Flexibility – One of the main drawbacks of a fixed exchange rate system is its lack of flexibility. Because the exchange rate is fixed, it cannot adjust to changes in market conditions or economic shocks.
- Central Bank Intervention – Another disadvantage of a fixed exchange rate system is that it requires constant central bank intervention. The central bank must buy and sell currencies in the foreign exchange market to maintain the fixed exchange rate. This can be costly and can drain the central bank’s foreign exchange reserves.
What is a Flexible Exchange Rate?
A flexible exchange rate system, on the other hand, is a monetary system in which the value of a currency is allowed to fluctuate freely in response to market forces. The exchange rate is determined by the supply and demand of the currency in the foreign exchange market. In a flexible exchange rate system, the central bank does not intervene in the foreign exchange market. It can also be known as a floating exchange rate.
Under this system, the country’s economic condition regulates and determines the market supply and demand for its currency. It is determined concerning other currencies which means the higher demand for a specific currency, the higher will be its exchange rate, and vice versa. So, therefore, the government and other monetary authorities have no control over the floating exchange rate.
Pros of Flexible Exchange Rate
- Automatic Adjustment – One of the primary advantages of a flexible exchange rate system is that it allows for automatic adjustment to changes in market conditions or economic shocks.
- No Central Bank Intervention – Another advantage of a flexible exchange rate system is that it does not require constant central bank intervention. The exchange rate is determined by market forces, and the central bank does not need to buy and sell currencies to maintain the exchange rate. This can reduce the central bank’s foreign exchange reserve requirements.
- Encourages International Trade – Flexible exchange rates can also encourage international trade. When the exchange rate is allowed to fluctuate freely, it can help to promote exports by making goods cheaper for foreign buyers.
Cons of Flexible Exchange Rate
- Exchange Rate Risk: One of the main disadvantages of a flexible exchange rate system is that this system may lead to uncertainty that businesses and individuals face due to fluctuations in the exchange rate. This uncertainty can make it more difficult to plan transactions and can increase the costs of doing business across borders.
- Price Instability: Another disadvantage of a flexible exchange rate system is that it can lead to price instability. When the exchange rate is allowed to fluctuate freely, it can make it more difficult for the central bank to control inflation.
Key Differences Between Fixed And Flexible Exchange Rate
While comparing fixed vs flexible exchange rate, here we have included some of the key differences between them, given as follows.
- Meaning – Fixed exchange rate refers to the nominal exchange system wherein the government and other monetary authorities like the central bank try to keep the rate of state currency fixed against the rate/value of other currencies. On the other hand, a flexible exchange rate is another monetary system wherein the exchange rate is set according to the supply and demand of money in the market.
- Control – The main difference between fixed and flexible exchange rates is the level of control that the government and central bank have over the exchange rate. In a fixed exchange rate system, the exchange rate is controlled by the government or central bank, whereas in a flexible exchange rate system, the exchange rate is determined by market forces.
- Effect on Currency Value – In a fixed exchange rate system, if the par value of the currency reduces, it is termed as devaluation, and if rises then it is known as revaluation. On the other hand, in a flexible exchange rate regime, the decrease in the currency value is termed as depreciation, and the increase, as appreciation.
- Difference Between Debit Card and Credit Card
- Difference Between Firm and Company
- Difference Between Transfer and Promotion
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between a fixed or flexible exchange rate system depends on a country’s economic and political circumstances. Fixed exchange rate systems provide stability, while flexible exchange rate systems allow for automatic adjustment to changes in market conditions. Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and it’s important to weigh them carefully to make an informed decision.




2 Comments