The difference between capital and revenue expenditures is often misunderstood by those who are not familiar with the financial world. There are many other subtle differences to consider as well, but in this article, we will focus on the difference between these two only of expenditures, i.e Capital and Revenue Expenditures.
You Can Also Read: Difference Between Capital Receipt and Revenue Receipt
What Is Capital Expenditure?
Capital expenditures (CapEx) are funds used by a company to acquire, upgrade, or extend the life of its physical assets, such as property, buildings, or equipment. These outlays are typically made in order to maintain or increase the value of the company’s operations.
CapEx is often contrasted with operational expenditure (OpEx), which refers to the costs incurred in running the day-to-day business of the company. While OpEx is typically incurred in pursuit of short-term goals, CapEx represents a company’s investments in long-term growth.
In general, companies will finance their CapEx through a mix of debt and equity. Since these expenditures can be significant, they can have a major impact on a company’s financial statement and cash flow. For this reason, it is important for investors to understand how a company is funding its capital expenditures.
Eight Characteristics Of Capital Expenditure
The eight major characteristics of capital expenditure are explained as follows.
- Capital expenditure (CapEx) is money used by a company to acquire, upgrade, or extend its long-term assets. This includes money spent on land, buildings, machinery, vehicles, and equipment. It also includes money spent on intellectual property, such as patents and copyrights.
- Capital expenditure is used to purchase or improve tangible assets.
- CapEx is a long-term investment.
- It is important for future growth and profitability.
- CapEx can be financed through debt or equity.
- Also, CapEx is typically recorded on the balance sheet as an asset.
- Depreciation expense is often used to account for the declining value of capital assets over time.
- Capital expenditures are not tax deductible like operating expenses
What Is Revenue Expenditure?
Revenue expenditure (RevEx) represents funds that are spent in pursuit of short-term goals. This includes expenses such as advertising, marketing, and product development. Revenue expenditure is typically incurred on a regular basis and does not directly increase the value of the company’s assets.
Revenue expenditure also includes the cost of goods sold (COGS), which is the direct cost associated with producing the goods or services that a company sells. COGS includes the cost of materials, labor, and overhead expenses.
Moreover, revenue expenditure can also be defined as all expenses that are incurred in order to generate revenue. This includes the cost of sales, marketing, and administration. Revenue expenditure is important to monitor as it can have a direct impact on the company’s bottom line. If Revenue expenditure is too high, it can eat into profits and lead to financial problems. Conversely, if revenue expenditure is too low, it could indicate that the company is not investing enough in its short-term goals and may miss out on opportunities for growth.
Ten Characteristics Of Revenue Expenditure
- Revenue expenditure is the amount spent on items that will be used up or consumed within the normal operating cycle of a business. This includes repairs and maintenance, salaries, rent, utilities, and other day-to-day expenses.
- Revenue expenditure is typically recorded as an operating expense on a company’s income statement.
- Secondly, revenue expenditure is recurring since the company spends it on a regular basis.
- Revenue Expenditure is for short-term purposes and is not capitalized.
- Revenue Expenditure does not result in the acquisition of any long-term assets.
- It does not generate any future economic benefits.
- Revenue Expenditures are incurred to keep the business running and are essential for its operation.
- Also, revenue expenditures are typically paid out of the company’s operating cash flow.
- Revenue Expenditures are often recorded as an expense in the company’s financial statements.
- Revenue Expenditures may be deducted for tax purposes.
Main Difference
The main difference between capital and revenue expenditures is their purpose and effect on financial statements. Revenue expenditures are incurred in order to keep a business running on a day-to-day basis, while capital expenditures are made in order to generate future revenue streams. While both types of expenses can impact a company’s bottom line, only capital expenditures can be used to generate new equity for shareholders.
You Can Also Read: Statement Of Affairs and Balance Sheet
Capital Vs Revenue Expenditure(Comparison Table)
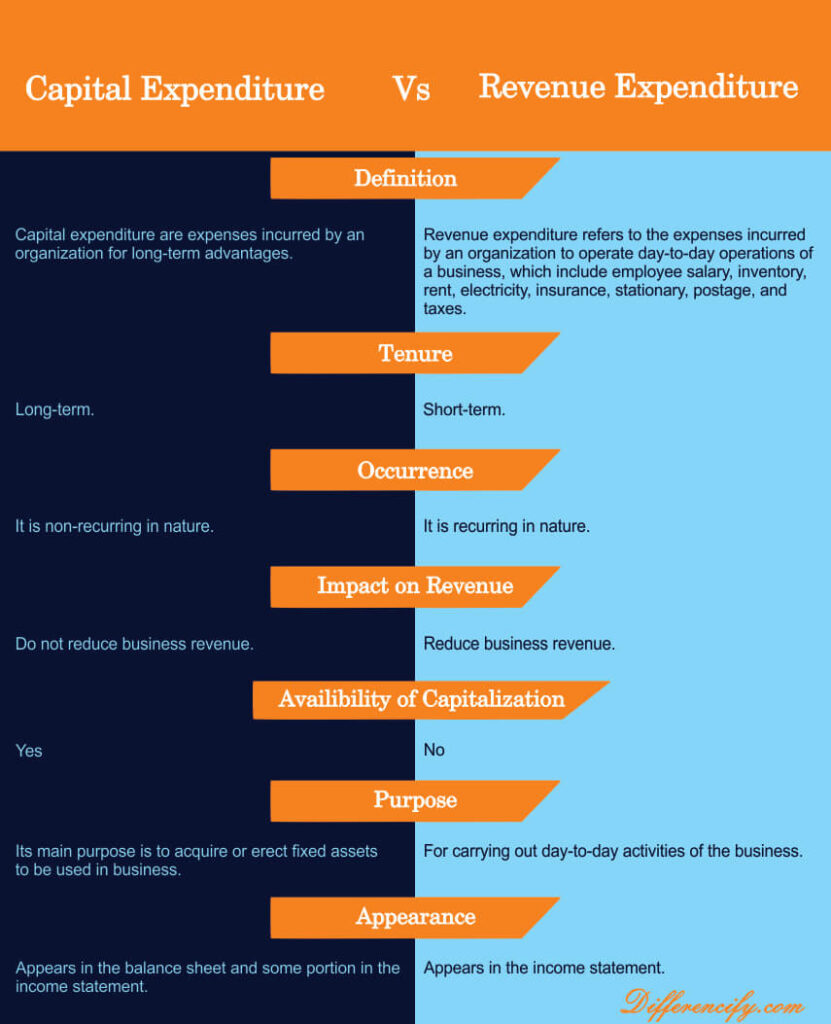
Key Differences Between Capital And Revenue Expenditure
The following points describe the key differences between capital and revenue expenditure.
- Definition – Revenue expenditure is the amount spent on items that will be used up or consumed within the normal operating cycle of a business. This includes repairs and maintenance, salaries, rent, utilities, and other day-to-day expenses. Capital expenditures, on the other hand, are investments in long-term assets such as property, equipment, or vehicles. These assets are not expected to be used up or consumed within the normal operating cycle of a business.
- Purpose – Capital expenditures are made to acquire or improve long-term assets such as property, equipment, or buildings. Revenue expenditures are incurred in the day-to-day operations of a business and are not intended to last beyond the current accounting period.
- Timing – Capital expenditures are typically made upfront, while revenue expenditures are incurred throughout the year as needed.
- Amount – Capital expenditures tend to be larger in dollar amount than revenue expenditures.
- Impact on Financial Statements – Capital expenditures typically result in an increase in assets and a decrease in cash on the balance sheet. Revenue expenditures result in an expense being recorded on the income statement.
- Treatment for Tax Purposes – Capital expenditures may be eligible for tax deductions, while revenue expenditures are not.
- Financing – Capital expenditures may be financed through loans or investments from shareholders, while revenue expenditures are typically paid for with operating cash flow.
- Examples – Some examples of capital expenditure items include land, buildings, machinery, vehicles, and office furniture. Common examples of revenue expenditure items include advertising, repairs and maintenance, utilities, and supplies.
- Recorded – Capital expenditures are typically recorded as a separate line item on a company’s balance sheet. On the other hand, Revenue expenditure is typically recorded as an operating expense on a company’s income statement
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that the main difference between capital and revenue expenditure is that capital expenditures are made in order to acquire or improve long-term assets. On the other hand, revenue expenditures are made in order to cover the costs of day-to-day operations. Capital expenditures require more careful planning and often involve a higher level of risk, but they can also lead to greater rewards in the form of increased revenues and profits.


5 Comments