Every business has both shareholders and stakeholders, but how exactly do these two groups differ? In this article, we’ll delve into the difference between shareholder and stakeholder, as well as present a helpful table to guide you in understanding their respective roles. Read on to learn more about each group and how they affect the success of a business.
You Can Also Read: Difference Between Share and Stock
What is a shareholder?
A shareholder also known as a stockholder is an individual or organization that owns shares in a company. Shares represent a portion of ownership in a company, and shareholders are entitled to a share of the company’s profits or losses.
Shareholders can be either natural persons or legal entities such as corporations. They may also be referred to as members, stockholders, or simply owners. Depending on the type of company, shareholders may have different rights and duties. For example, in a public company, shareholders elect a board of directors to oversee the management of the company.
Types Of Shareholder
A shareholder is an individual or organization that owns at least one share of a company’s stock. Common shareholders and preferred shareholders are two different kinds of shareholders.
- Common shareholders have voting rights and may receive dividends, but they have no guarantee of receiving their investment back if the company goes bankrupt.
- Preferred shareholders have no voting rights, but they are typically guaranteed a fixed dividend and they have priority over common shareholders if the company is liquidated.
Shareholder Theory
The shareholder theory is the idea that the only purpose of a corporation is to maximize shareholder wealth. This theory is based on the assumption that shareholders are the only stakeholders with a financial interest in the corporation.
The shareholder theory is also known as the stockholder theory or the shareholder primacy theory. It is opposed to the stakeholder theory, which takes into account the interests of all stakeholders when making business decisions.
The shareholder theory has been criticized for its single-minded focus on shareholder wealth and for ignoring the interests of other stakeholders. This can lead to decisions that may be good for shareholders in the short term but bad for employees, customers, suppliers, and society in general in the long term.
What is a stakeholder?
A stakeholder is anyone who has an interest in the success or failure of a company. This includes shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, creditors, and even the community where the business is located. While shareholders are stakeholders, not all stakeholders are shareholders.
For a business to be successful, it must create value for all of its stakeholders, not just shareholders. Value can be created in many ways, such as through providing good jobs, offering high-quality products and services, being a good corporate citizen, and so on. When a company creates value for all of its stakeholders, it is said to have created shareholder value.
Types of Stakeholder
A stakeholder is any individual or group that has an interest in the success or failure of a business. There are two types of stakeholders: internal and external stakeholders.
- Internal stakeholders are those who are directly involved with the company and its operations. This includes owners, shareholders, board members, employees, and management. They have the most direct impact on the decisions and actions of a company.
- External stakeholders are people or organizations outside of the organization that can still be impacted by its actions. This may include customers, suppliers, lenders, investors, governments, and communities. These stakeholders may not have direct input on a company’s decisions but their opinions can still affect the way it does business.
Stakeholder Theory
The Stakeholder Theory is a theory of organizational management and business ethics that addresses the moral obligations an organization has to its stakeholders, which are any individuals or groups who may affect or be affected or influenced by the organization’s actions.
The theory was originally proposed by R. Edward Freeman in the 1984 book Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach, and has been further developed by other scholars such as Michael Porter and Lynn Stout.
There are three key concepts in stakeholder theory:
- The first is that organizations are not just moral agents of their shareholders, but have moral responsibilities to all of their stakeholders.
- The second is that businesses should be managed for the long-term benefit of all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
- The third is that stakeholder management is a process of creating value for all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
Shareholder Vs Stakeholder(Comparison Table)
The following table shows the exact comparison table between shareholder and stakeholder.
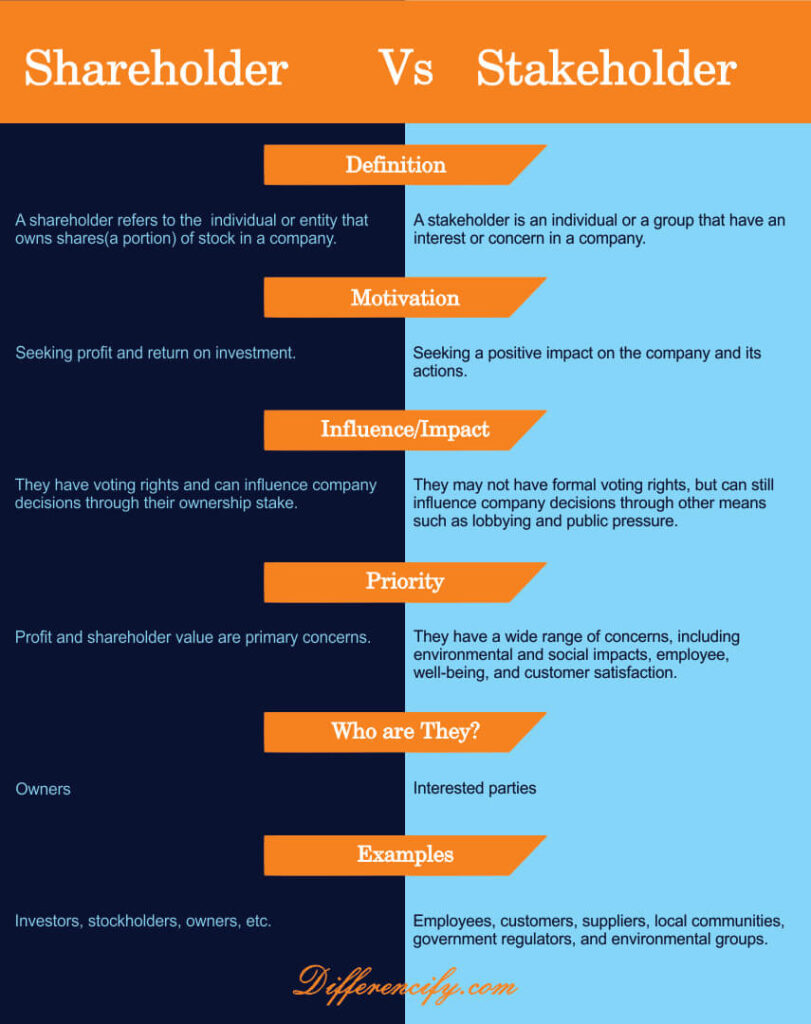
Key Difference between Shareholder and Stakeholder
There are numerous key differences between shareholders and stakeholders, which are summarized as follows.
- Shareholders are owners of the company who have invested their money in purchasing shares. On the other hand, Stakeholders are individuals or organizations that have an interest in the success or failure of a company. This includes employees, suppliers, customers, lenders, and the community at large.
- Secondly, shareholders have a financial stake in the company and want to see it generate profits so that they can get a return on their investment. On the other hand, stakeholders do not have a financial stake in the company but may be impacted by its actions nonetheless.
- Shareholders wield considerable power within the company and can make decisions about its direction and strategy. In contrast, stakeholders don’t have as much power as shareholders, but they can still exert Influence over the company through things like consumer boycotts or public pressure campaigns.
- Shareholders are typically more concerned with short-term results rather than long-term sustainability. On the other hand, stakeholders are interested in seeing the company succeed over the long term since their livelihoods may depend on it. However, there may also be some short-term oriented stakeholders such as hedge funds that take speculative positions in companies.
- Shareholders can be either individuals or institutions such as banks or pension funds. On the other hand, stakeholders are typically individuals or organizations such as labor unions, non-profit organizations, local governments, and so on.
You Can Also Read: Difference Between Bonds and Debentures
Bonus Concepts
Business and Finance enthusiasts can also read the following two bonus concepts.
What is Shareholder Value?
Shareholder value is the increase in the value of a company’s shares over time. It is measured by the share price, which is the price of a single share of the company’s stock. The share price is determined by supply and demand in the stock market, and it can fluctuate daily.
Shareholder value is important to shareholders because it represents their investment in the company. It is also important to the company itself because it shows how well the company is doing financially. Shareholder value can be used to compare different companies or to measure the performance of a single company over time.
How to Improve Shareholder Value?
There are several ways to increase shareholder value, including increasing profits, paying dividends, reducing expenses, and repurchasing shares.
Increasing profits will cause the share price to rise while paying dividends will give shareholders a direct return on their investment. Reducing expenses will improve the bottom line and make the company more efficient while repurchasing shares will reduce the number of shares outstanding and make each one worth more.
Improving shareholder value is not always easy, but it is important for both shareholders and companies. By doing so, companies can ensure that their investors are happy and that they are making money.
What is Stakeholder Value
Stakeholder value, on the other hand, takes into account the interests of all parties that have a stake in the company, not just shareholders. There are several reasons why companies should focus on creating stakeholder value rather than just shareholder value.
- First, it’s important to remember that shareholders are not the only people who are affected by a company’s performance. Other stakeholders, such as employees, customers, vendors, and the community all have an interest in the success of a business.
- Secondly, focusing on stakeholder value can increase loyalty and engagement from these groups, which can lead to better customer service and improved employee retention.
- Lastly, creating stakeholder value can help companies improve their reputation and build relationships with key stakeholders that can benefit the business in the long run.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that the key difference between shareholders and stakeholders is in their legal status. Shareholders are legally entitled to certain rights by virtue of owning shares in a company, such as voting rights and dividend payments. On the other hand, stakeholders have no such legal entitlements but still have an interest in the success of the business.
Although their roles may overlap at times, it is important to distinguish between the two when considering any decisions that may affect either group. A clear understanding of shareholder vs stakeholder will ensure that all parties involved can be considered equally and fairly when making vital organizational decisions. Thank you so much for scanning the difference between shareholder and stakeholder through our article. Hope you have clearly understood the differences between these two terms.
You Can Also Study the Blog: For Investment Decisions


3 Comments